Biomolecular Motors
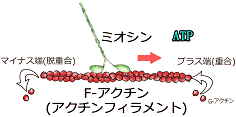
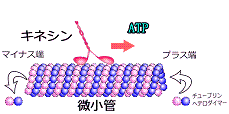
Biomolecular motors are molecular machines that can convert chemical energy of ATP into mechanical work. Biomolecular motors are classified mainly into three groups- translational motors, rotary motors and polymerization motors. So far, we have been focusing on the translational bimolecular motor systems actin-myosin and microtubule-kinesin. Actin and microtubule are cytoskeletal filaments polymerized from actin monomer (Globular actin) and tubulin dimer (α and β tubulin) respectively, whereas myosin and kinesin, dynein are corresponding motor proteins for actin and microtubule respectively. Myosin and kinesin can move along actin and microtubule filaments in one direction by consuming the chemical energy of ATP. Actin-myosin plays important role in cell motility, cell shape determination, muscle contraction, etc. while microtubule-kinesin system is mainly involved in cellular transport, cell division, etc.