Ultimate utilization and conversion
of energy is our research target.
About Us
We are pioneering electrode reaction systems that are directly linked to efficient renewable energy production. We are developing new materials for nanostructured electrodes, high-precision electrode reaction measurements, advanced high-sensitivity spectroscopy, and novel theories of surface electron transfer processes to break through the upper limits of existing energy conversion capabilities. We are also creating systems that can freely control the flow of electrons, light, and ions, thereby creating a new scientific theory for the extreme use of energy that is not bound by the properties of existing material systems.
News
- 2026-02-18News
Students (B3) who have been assigned to the Physical Chemistry Laboratory are requested to come to the seminar room on the 7th floor of Science Building No. 6 at 13:00 on Thursday, February 19.
Please bring writing materials and your laptop computer with you.
- 2026-01-10NewsPublicationH. Minamimoto, H. Ooka, D. Ohta, S. Utsumi, M. Homma, K. Murakoshi, and M. Mizuhata, “Mechanistic Elucidation of the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Ni–Mo Alloys via Surface and Data-Driven Kinetic Analyses" J. Phys. Chem. C, accepted (2026).
- 2025-12-22NewsPublicationD. Ashizawa, D. Kurosu, M. Itatani, N. Oyamada, D. Sato, R. Kamada, K. Sakaguchi, T. Fukushima, and K. Murakoshi “Deep Learning-Assisted Tracking of Bubble Dynamics for Elucidating Oxygen Evolution Reaction on Nickel Electrodes" J. Electroanal. Chem., in press (2025). DOI : 10.1016/j.jelechem.2025.119760
- 2025-10-18NewsPublicationN. Oyamada, H. Minamimoto, and K. Murakoshi “Formation of Distinct Condensed Molecular Phases at Solid-Liquid Interfaces by Plasmon-Driven Molecular Trapping under Ambient Conditions" Chem. Sci., 16, 22611-22620 (2025). DOI : 10.1039/D5SC05604Ga
- 2025-10-18NewsPublicationM. Itatani, N. Iwasa, N. Miyasaka, L. Takahashi, K. Takahashi, T. Fukushima, and K. Murakoshi “Temperature-Tunable Fabry–Perot Cavity for Aqueous Systems" Res. Chem. Interm., in press (2025).
Research

Electrochemical fine-tuning of strong coupling state
When the dye molecules exist at the surface of the metal nano structure and the energy of the dye excitions are close to that of plasmon, the new energy hybridized state generate which is called strong coupling generates due to the electronic interactions between the excition and plasmon. This new state provides the new photo response property beyond the limitation of the system. Recently, we have tried to electrochemically tune the coupling strength for the efficient use of the light energy.
Plasmonic single molecular trapping
With the excitation of the LSPR, the strong electromagnetic field with the sharp spatial gradient can be generated. Recently, several theoretical studies predict that the even small molecules could be trapped within this field. In our lab., we have attempted to establish the plasmonic molecular optical trapping method via electrochemical surface-enhanced Raman scattering measurements.

Establishment of the novel photo conversion system
The efficiency of the photo conversion for the semiconductor electrode is often limited to the narrow wavelength region due to its wide band gap energy. Recently, plasmonic photo-conversion system which is the combination of the plasmonic metal nano-structures with the wide band gap semiconductor, e.g. TiO2, have been receiving much attention. In our lab., we have introduced several techniques, such as the photo-induced oxidation polymerization or Raman measurements, to understand the detail about the charge transfer process in the system.
Publications
 [2] H. Minamimoto, H. Ooka, D. Ohta, S. Utsumi, M. Homma, K. Murakoshi, and M. Mizuhata,
[2] H. Minamimoto, H. Ooka, D. Ohta, S. Utsumi, M. Homma, K. Murakoshi, and M. Mizuhata,
“Mechanistic Elucidation of the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Ni–Mo Alloys via Surface and Data-Driven Kinetic Analyses"
J. Phys. Chem. C, accepted (2026).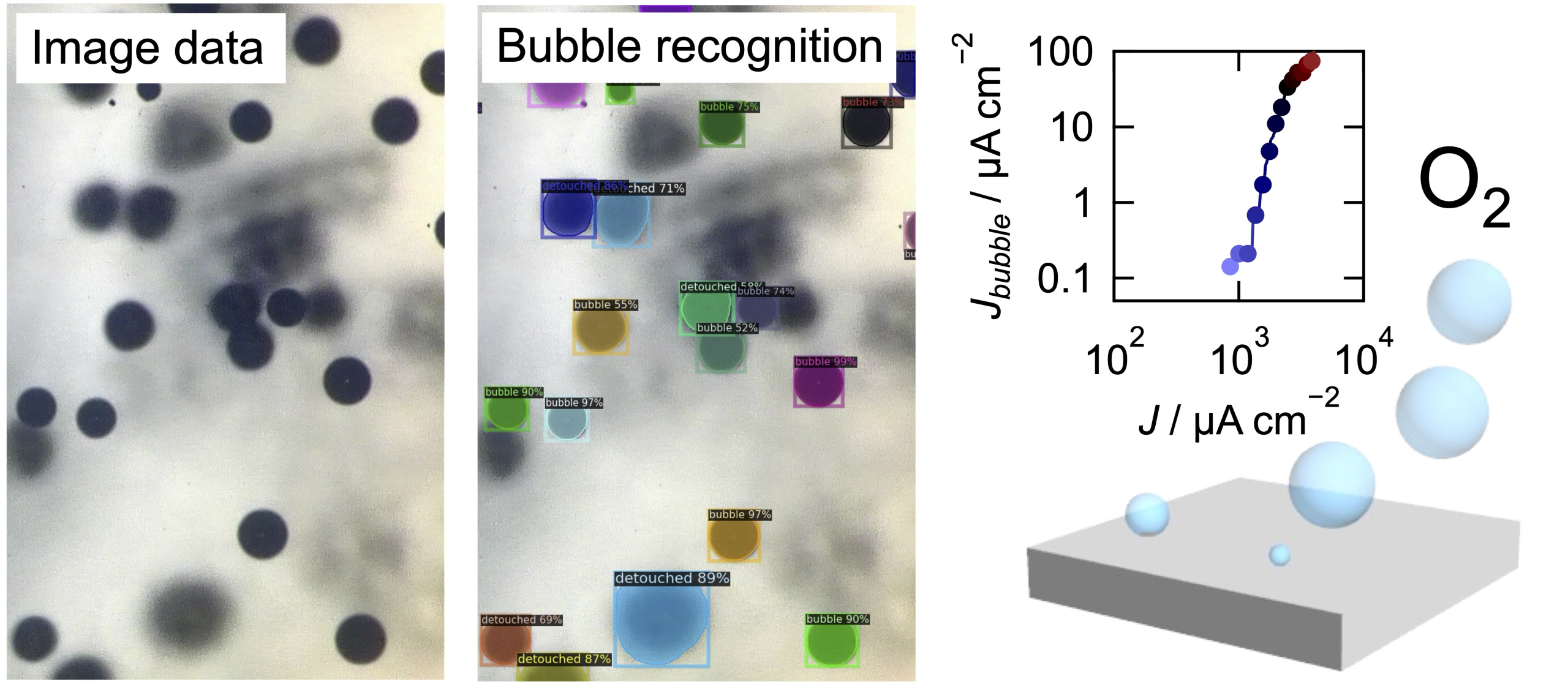 [5] D. Ashizawa, D. Kurosu, M. Itatani, N. Oyamada, D. Sato, R. Kamada, K. Sakaguchi, T. Fukushima, and K. Murakoshi
[5] D. Ashizawa, D. Kurosu, M. Itatani, N. Oyamada, D. Sato, R. Kamada, K. Sakaguchi, T. Fukushima, and K. Murakoshi
“Deep Learning-Assisted Tracking of Bubble Dynamics for Elucidating Oxygen Evolution Reaction on Nickel Electrodes"
J. Electroanal. Chem., in press (2025).
DOI : 10.1016/j.jelechem.2025.119760 [4] N. Oyamada, H. Minamimoto, and K. Murakoshi
[4] N. Oyamada, H. Minamimoto, and K. Murakoshi
“Formation of Distinct Condensed Molecular Phases at Solid-Liquid Interfaces by Plasmon-Driven Molecular Trapping under Ambient Conditions"
Chem. Sci., 16, 22611-22620 (2025).
DOI : 10.1039/D5SC05604Ga [1] M. Itatani, N. Iwasa, N. Miyasaka, L. Takahashi, K. Takahashi, T. Fukushima, and K. Murakoshi
[1] M. Itatani, N. Iwasa, N. Miyasaka, L. Takahashi, K. Takahashi, T. Fukushima, and K. Murakoshi
“Temperature-Tunable Fabry–Perot Cavity for Aqueous Systems"
Res. Chem. Interm., in press (2025).
